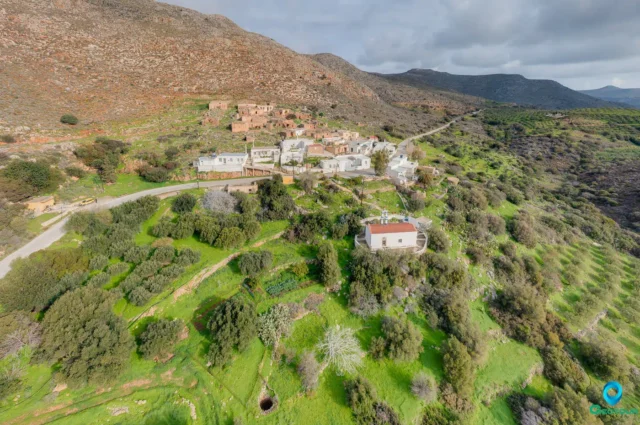
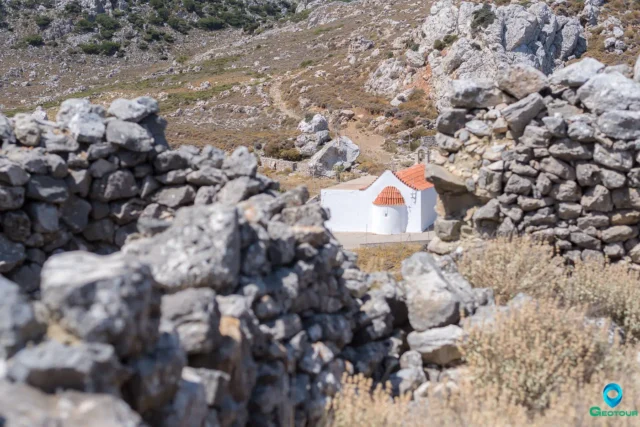
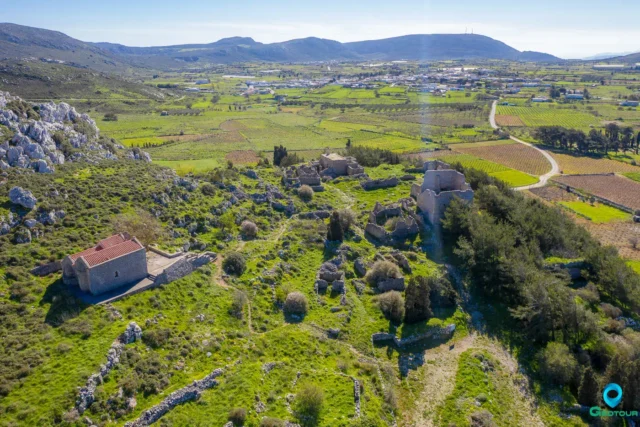
135
listings found
Categories
Active filters:
Mochlos, Siteia
Mochlos Island, a small rocky island in Crete's Gulf of Mirabello, is a significant Minoan archaeological site and a popular tourist destination. Inhabited during Minoan times, Mochlos was a major port and production center. The Minoan settlement was impacted by the Thera eruption. Later, Venetians built a fort, whose ruins remain. The island's history spans from the Bronze Age Minoan civilization through Venetian rule to its current status as a tourist attraction. The village of Mochlos faces the island.
Papagiannades, Siteia
Papagiannades, a village in Sitia, Crete, boasts a history dating back to the Minoan era, evidenced by settlement remains. First mentioned in 1834, its name derives from its settlers. The Venetian-era church of Panagia Eleousa, with frescoes from 1363-64, stands as a landmark. Known for high-quality olive oil, the village features a historic oil mill. Papagiannades offers a glimpse into traditional Cretan life, with narrow streets and hospitable residents, surrounded by olive groves. The village population, 69 in 2021, reflects its quiet charm.
Zakathos, Siteia
Zakathos, a now-abandoned village in Lasithi, Crete, has a history rooted in pre-Hellenic times. During the Ottoman era, it was a Turkish village, with inhabitants converting to Islam. Later, it functioned as a metochi (farm) associated with Katelionas, as documented in the 1583 census. The village, situated in the Sitanos region, had a Muslim population of 103 in 1881. The abandoned settlement, divided into Upper and Lower Zakathos, is now utilized by residents of Ziros and Zakros. A notable Ottoman-era fountain graces the nearby "Vrysi" spring in Sitanos.
Klisidi, Siteia
Klisidi, a settlement in Sitia, Lasithi, Crete, is located at 220 meters altitude. While not in Venetian or early Ottoman records, it's mentioned in a later Ottoman document and the 1834 Egyptian census with 5 Christian families. In 1881 it had 37 Christians, growing to 44 inhabitants by 1900. The population has since decreased, from 49 in 1940 to just 2 in 2021.
Kellaria, Siteia
Kellaria, a small village in the Sitia municipality of Lasithi, Crete, is situated at an altitude of 340 meters. Known for olive oil and wine production, the village's history dates back to 1583. Once an independent municipality, it later became part of Sitia. The village is divided into inhabited and abandoned sections, showcasing traditional architecture. Its population has dwindled to just four residents in 2021. The Agios Georgios church and a cemetery are located within the village. Historically, inhabitants were farmers and shepherds. Kellaria is near the Zakros archaeological site and Vai beach.
Skalia, Siteia
Skalia, a small village in Crete's Sitia region, is known for its 19th-century resistance against Turkish rulers. The villagers' bravery became legendary, but their resistance led to a tragic end. Betrayed by a priest, the villagers were massacred by Turks. Today, Skalia lies in ruins, with only the Church of Agios Georgios and one house remaining. The village wall and spring are still visible. The tragedy occurred in the late 17th or early 18th century, and is commemorated annually.
Monastiraki, Ierapetra
Monastiraki (Monastirakion) is a small village in Lasithi, Crete, situated on Mount Thrypti's slopes, near Ha Gorge, with views of Mirabello Gulf. Located 5km from Pahia Amos and 11km from Ierapetra, it's part of the Pahia Amos community. Historically, it was mentioned by Castrofylakas around 1853, possibly built on a former monastery site dedicated to Saints Constantine and Helen. The 2021 census recorded 21 residents. The village experienced population fluctuations over the years, from 10 families in 1834 to a single resident for some time, and now sees a revival with home renovations and infrastructure improvements. Points of interest include the Byzantine churches of Agios Stefanos and Agios Georgios, alongside two traditional cafes serving Cretan cuisine.
Thrypti, Ierapetra
Thrypti is a small mountain settlement in eastern Crete, within the municipality of Ierapetra, Lasithi. Nestled in the Thrypti mountains, near the Ha Gorge and Afentis Christos peak, it boasts a unique pine forest. The village has historical significance, with evidence of Minoan and Byzantine settlements. Landmarks include the churches of Nativity of Theotokos, Agios Ioannis Prodromos, Timios Stavros, and Agia Anna. The economy is based on viticulture and animal husbandry, though many residents have relocated. Access is via paved road from Pano Chorio and dirt roads from Oreino and Kavousi.
Etia, Sitia
Etia, located in the Armeni municipality in eastern Crete, is an uninhabited village with a rich history dating back to the Byzantine era. Known for its well-preserved Venetian mansion, the De Mezzo, Etia was once a major settlement. The village also features the churches of Agia Aikaterini and Agios Ioannis, both bearing traces of Byzantine wall paintings. The De Mezzo mansion, a significant example of Venetian architecture, has undergone extensive restoration. Etia, though deserted, remains a protected traditional settlement and a testament to Crete's diverse heritage.
Voila abandoned village
Voila, an abandoned village near Chandras in Sitia, Crete, offers a glimpse into Crete's Venetian and Ottoman past. The village, deserted since the 19th century, likely owes its name to a Byzantine surname, a term for boyars, or a place for oxen. Voila was once a sizeable village, documented in Venetian censuses of the 16th century with over 300 inhabitants. A prominent landmark is the Venetian tower, featuring a 1742 Turkish inscription and carvings of axes, cypresses, and pentagrams. Local tradition links the tower to a Janissary named Tsin-Alis. The village also houses the ruins of the 15th-century church of Agios Georgios and Panagia, likely built by the Salamon family, potential ancestors of the poet Dionysios Solomos. Two fountains with Turkish inscriptions and remnants of a Venetian castle further illustrate Voila's rich history.
The Archaeological Collection of Ierapetra
The Archaeological Collection of Ierapetra, housed in the former Ottoman School built in 1899, offers a captivating journey through the history of the region, from the Bronze Age to the […]
The Archaeological Museum of Agios Nikolaos
The Archaeological Museum of Agios Nikolaos, Crete, houses a remarkable collection of artifacts spanning from the Neolithic period to the end of the Greco-Roman era. Established in 1970, the museum showcases the evolution of art and culture in Eastern Crete. The collection includes finds from the Early Minoan cemetery of Agia Fotia and the Minoan palace of Malia. One of the most renowned objects is the "Goddess of Myrtos," a unique libation vessel from the Pre-palatial period. The museum's rectangular building features eight exhibition halls arranged around a central atrium, facilitating a clear and intuitive flow for visitors. The museum actively engages with the public through temporary exhibitions and educational programs. It is open from 08:30 to 15:30, closed on Tuesdays. Ticket prices vary depending on the season, with combined tickets available for multiple archaeological sites and museums in the region.
The Archaeological Museum of Siteia
The Archaeological Museum of Siteia, established in 1984, serves as a vital repository of the rich history of eastern Crete. Born from the dedication of local communities and authorities, the […]
Olous
Olous, an ancient Cretan harbor city, now largely submerged off the coast of Elounda, was inhabited from the Early Minoan period through the Hellenistic period. Its strategic location in the Mirabello Gulf made it a significant maritime hub, connecting the Eastern and Western Mediterranean. Archaeological investigations, including underwater surveys, have revealed remnants of Minoan cemeteries, fortifications, and possible public buildings. The city's history is intertwined with that of other Cretan powers like Knossos and Lato. Olous was known for its temple to Britomartis and its connections with Ptolemaic Egypt. Today, the site offers a glimpse into Crete's rich maritime past.
Hierapytna
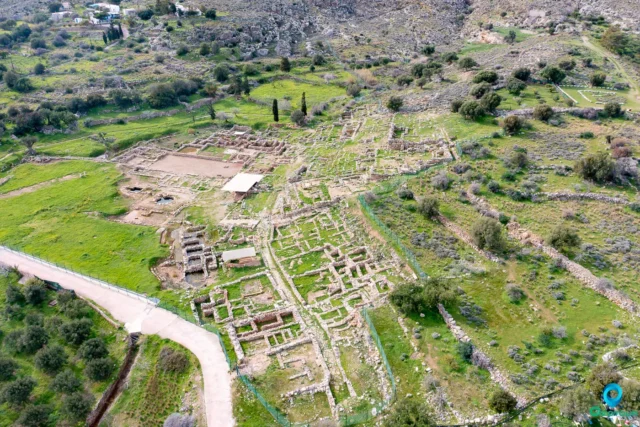
Hierapytna, located on the southern coast of Crete, was founded in the Geometric period (c. 9th century BC). The city was a major hub for trade and commerce in ancient times and played a significant role in the island's political and military affairs. Hierapytna flourished during the Hellenistic and Roman periods. It became part of the Byzantine Empire after the division of the Roman Empire. Following the Arab conquest of Crete in the 9th century, Hierapytna was abandoned. Modern archaeological investigations have revealed a wealth of information about the city, including its city walls, agora, temple, theater, and private houses.
Mardati, Agios Nikolaos
Mardati is a settlement located in the Lasithi regional unit on the island of Crete, Greece. It belongs to the Municipality of Agios Nikolaos
Voulismeni, Agios Nikolaos
Voulismeni is a settlement located in the Lasithi regional unit on the island of Crete, Greece. It belongs to the Municipality of Agios Nikolaos
Vrachasi, Agios Nikolaos
Vrachasi is a settlement located in the Lasithi regional unit on the island of Crete, Greece. It belongs to the Municipality of Agios Nikolaos
Dreros, ancient city
Dreros, also known as Driros, is an archaeological site near Neapoli in Crete, significant for its post-Minoan remains from the early Archaic Period. Flourishing from the 8th to 6th centuries BC, Dreros was an important center of trade and culture, known for its harbor, temples, bronze working, and pottery. The city, built on two hills, features a sanctuary dedicated to Apollo Delphinios, where 8th century BC bronze statuettes of Apollo, Artemis, and Leto were discovered. A large, open cistern, possibly used for ritual purposes, was found in the agora, the city's public gathering space. Inscriptions reveal a board of officials called the 'Twenty of the Polis' and the division of the people into 'phylai' or tribes. The site includes one of the earliest known examples of a Greek temple, dedicated to Apollo Delphinios. Dreros declined in importance after the 6th century BC and was eventually abandoned.
Kato Metochi, Lasithi plateau
Kato Metochion is a settlement located in the Lasithi regional unit on the island of Crete, Greece. It belongs to the Municipality of Lasithi plateau