34
listings found
Categories
Active filters:
Galifa, Chersonissos
Galifa is a settlement located in the Heraklion regional unit on the island of Crete, Greece. It belongs to the Municipality of Chersonissos
Chochlakies, Chersonissos
Chochlakies is a settlement located in the Heraklion regional unit on the island of Crete, Greece. It belongs to the Municipality of Chersonissos
Potamies, Chersonissos
Potamies (Ποταμιές) is a historic Cretan village in Chersonissos, near Heraklion. Mentioned in the 1583 Castrofylakas census, it features the abandoned Byzantine monastery of Panagia Gouverniotissa, with preserved frescoes, and the 15th-century church of the Transfiguration of the Savior. The village sits on the Aposelemis River, amid olive groves and lush vegetation. Its history includes Venetian influence, with a notable aqueduct supplying ancient Chersonissos. Potamies offers traditional Cretan cuisine and hospitality, with cultural events held at the monastery. The nearby Aposelemis Dam and the Dikti Natura 2000 area add to its appeal. The village's population has fluctuated over time, from 153 in 1583 to 348 in 2021.
Krasi, Chersonissos
Krasi is a settlement located in the Heraklion regional unit on the island of Crete, Greece. It belongs to the Municipality of Chersonissos
Mochos, Chersonissos
Mochos is a settlement located in the Heraklion regional unit on the island of Crete, Greece. It belongs to the Municipality of Chersonissos
Episkopi, Chersonissos
Episkopi, a village near Heraklion, Crete, has a long history dating back to the Minoan era. The village's name, meaning "bishopric", reflects its role as the seat of the Bishop of Hersonissos after the Byzantine era. It has numerous Byzantine and post-Byzantine churches, including the 11th-century Panagia Kera-Limniotissa and the 14th-century Agios Ioannis with Venetian-era frescoes. Episkopi also has a war museum and a municipal park.
Malia, Chersonissos
Malia is a settlement located in the Heraklion regional unit on the island of Crete, Greece. It belongs to the Municipality of Chersonissos
The Aqueduct of Chersonesos
Discover the ancient aqueduct of Chersonesos in Crete, a marvel of Roman engineering that supplied water to the city for centuries. Learn about its construction, significance, and connection to the broader Roman presence on the island.
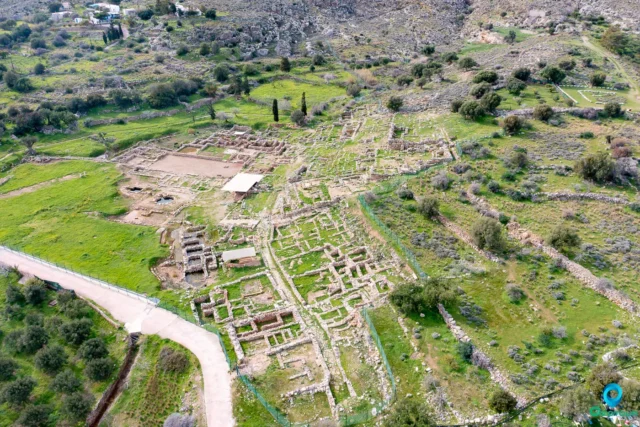
Malia Minoan Palace
The Minoan archaeological site at Malia, located on the northern coast of Crete, is a significant site for understanding the Bronze Age civilization. The Palace of Malia is the third largest Minoan palace discovered. The palace and surrounding town and cemeteries offer a glimpse into the complex social, political, economic, and religious structures of Minoan society. The area was inhabited as early as the Early Neolithic period. The first monumental architecture at Malia, often referred to as the Old Palace, dates to the Early Minoan IIB period. This structure, or group of structures, was built around a large open space, sharing the same alignment as the later palace. The second palace, whose ruins are visible today, was built in the Late Minoan IA period, around 1650 BCE. It was constructed on the ruins of the Old Palace, inheriting its basic layout and orientation. The palace's central court, a defining feature of Minoan architecture, is oriented north-south. The New Palace at Malia met its demise around 1450 BCE, coinciding with the destruction of other Minoan sites across Crete. The cause of this widespread destruction remains a topic of scholarly debate.
Minoan Shipyard at Agii Theodori
The Minoan civilization on Bronze Age Crete heavily relied on maritime prowess, establishing extensive Mediterranean trade networks with Egypt, Cyprus, and the Levant through advanced shipbuilding and strategic harbor towns. The archaeological site at Agii Theodori, on Vathianos Kambos beach near Heraklion, exemplifies this. Dating to the Late Minoan I period (c. 1600-1450 BC), it features a significant, carved dry dock (approx. 48m x 11m) and timber storage areas, indicating a dedicated shipyard. Its peninsula location offered protection and sea access. This site, near the Palace of Knossos and the port of Amnisos, underscores Minoan maritime dominance, shipbuilding ingenuity, and the vital role of coastal settlements in their economic and cultural expansion.
Amnisos Villa of the Lilies
Amnissos, an ancient Minoan port city located on Crete's north coast, boasts the luxurious Villa of the Lilies. This two-story villa, constructed with ashlar blocks during the Middle Minoan IIIA period (around the 17th century BC), features a hall with multiple doors, a bathroom, stairs, and covered paved areas. Its name comes from the frescoes of lilies that once decorated its walls. The villa, excavated in 1932 by Spyridon Marinatos, was likely destroyed by an earthquake or tidal wave around 1500 BC. Amnissos is also significant for its mythological connection to Zeus, whose omphalos (navel) is said to have fallen there. The area was referred to as the Omphalian Plain. The name Amnissos appears in Linear B inscriptions, indicating its importance to the Minoan civilization. The presence of the harbor, various buildings, and an open-air archaic sanctuary dedicated to Zeus further underscores its historical significance.
Amnisos Sanctuary of Zeus Thenatas
The Sanctuary of Zeus Thenatas at Amnisos, located on the north-central coast of Crete near Heraklion, is an archaeological site with a rich history spanning from the Bronze Age to the Early Iron Age. The sanctuary is dedicated to Zeus Thenatas, a deity associated with both Minoan and Mycenaean traditions. Amnisos, mentioned in Homer's Odyssey, was a significant center for maritime activities and trade during the Bronze Age. Excavations have revealed a 44-meter-long ashlar wall, smaller podia, and a thick layer of ash and burnt animal bones, suggesting animal sacrifice and ritual feasting. Votive offerings include bronze tripods, figurines, miniature weapons, and terracotta figurines of bulls and horses. The sanctuary exemplifies the continuity and change in Cretan religious practices, with the site's dedication to Zeus Thenatas reflecting Minoan traditions, while the adoption of new votive practices and the presence of faience objects highlight the evolving nature of religious expression. The sanctuary was operational from the Protogeometric period (c. 900 BC) to the end of the Early Iron Age (c. 600 BC), with two main phases of use marked by the construction of two temples: Temple A (Late Subminoan period to around 800 BC) and Temple B (around 800 BC to c. 600 BC).
Karphi archaeological site
Karphi, a Late Minoan IIIC refuge village in Crete, perched high above the Lasithi Plateau, offers a glimpse into Minoan resilience during a time of upheaval. Excavated in the late 1930s, the site reveals a planned settlement with houses, streets, and evidence of diverse cult activities. Its strategic location provided a defensive advantage, offering panoramic views of the Lasithi plain and north-central Crete. The village likely served as a refuge for Minoans seeking safety and survival after the collapse of the Minoan palaces. Despite the harsh conditions, the village featured paved streets, yards, and single-story houses, suggesting a planned and organized community. Karphi stands out for its diverse and widespread cult activities, with shrines dedicated to goddesses and various ritual artifacts. The Temple served as the central focus for ritual activities, housing goddess figures, snake tubes, braziers, and fireboxes. Other areas, such as the Commercial Quarter and the Great House Shrine, also contained evidence of cult practices. Rooms containing offering stands, figurines, and libation vessels indicate that rituals were not confined to formal shrines, suggesting a more informal setting for community offerings. This decentralized approach to ritual practices distinguishes Karphi from other LM IIIC sites.