107
listings found
Categories
Active filters:
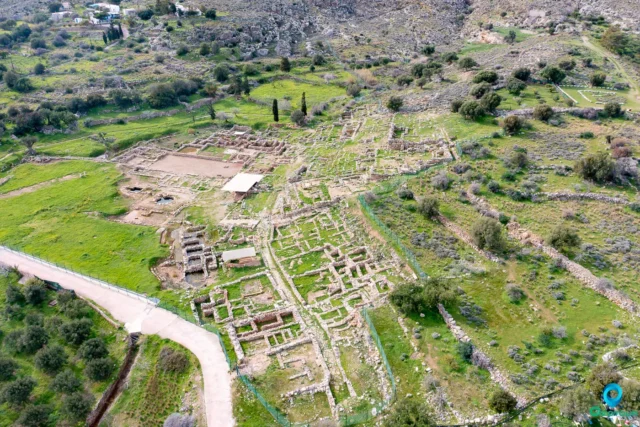
Ancient Arkadia
Ancient Arkadia (Arcades) was a significant polis on Crete, located near modern Afrati. It contested Mount Ida's claim as Zeus's birthplace. Active from at least the 4th century BCE (noted by Theophrastus for environmental issues), it participated in the Lyttian War (c. 220 BCE) and minted silver/bronze coins inscribed "ARKADON" (c. 330-280/70 BCE). Numerous inscriptions reveal treaties with Gortyn, Miletos, Teo, and Eumenes II (183 BCE), plus Roman-era bathhouse regulations. Excavations uncovered houses, a cemetery with Minoan-influenced vaulted tombs, Geometric/Orientalizing period artifacts, local pottery, and a unique 7th-century BC Phoenician capital. Epigraphic evidence suggests an Asclepius temple.
Chersonissos, Herronissos (Ancient)
Chersonissos is an ancient Greek city located on the northern coast of Crete. It was inhabited as early as the Minoan period and continued to flourish under the Romans and Byzantine eras. The city served as the port of Lyttos, an inland city, and was an important center for trade and commerce. Archaeological excavations have revealed a number of significant structures, including a theater, early Christian basilicas, and harbor remains. The city's history is reflected in its coins, which feature various deities and symbols. Chersonissos is now a popular tourist destination, known for its beautiful beaches, ancient ruins, and lively nightlife.
Gerokampos Tholos Tomb
The Lebena Gerokampos Tholos Tomb is an Early Minoan I-II (c. 3100-2600 BCE) archaeological site located near Lentas, on the southern coast of Crete, close to the ancient Minoan settlement of Lebena. The tomb, with an interior diameter of approximately 5 meters, is typical of tholos tombs, with a circular chamber built of large stones and a corbelled vault. The tomb also features several smaller chambers or annexes, which were added later. These annexes, along with the main tholos, served as spaces for burial and ritual activities. A large quantity of pottery, including pyxides, tankards, cups, and bowls, was found in the tomb. The tomb contained the skeletal remains of numerous individuals, providing evidence of collective burial practices. Other significant finds from the tomb include jewelry, tools, and figurines.
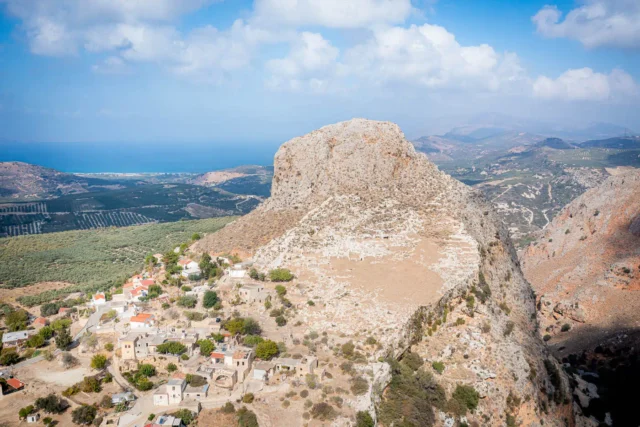
Vrysinas Peak Sanctuary
The Vrysinas Peak Sanctuary, located on the slopes of Mount Vrysinas in Crete, is a significant archaeological site that offers valuable insights into Minoan religion and culture. Excavations have revealed a wealth of artifacts, including human and animal figurines, pottery, horns of consecration, and a fragment of a libation table with a Linear A inscription. The sanctuary's unique position as the sole Neopalatial peak sanctuary in the region highlights its importance in the religious landscape of Minoan Crete. The site is easily accessible to visitors and provides a fascinating glimpse into the spiritual world of the Minoans.
The Necropolis of Phourni
The Phourni necropolis, near Archanes, Crete, is a significant Minoan burial site used from the Early Minoan II (EM II) to the Late Minoan IIIC (LM IIIC) periods. It features a variety of tomb types, including tholos tombs, rectangular tombs, and composite tombs, reflecting the evolution of Minoan funerary architecture and burial practices over time. Tholos tombs are beehive-shaped structures used for collective burials, while rectangular tombs resemble houses, suggesting a symbolic connection between the house of the living and the house of the dead. Composite tombs combine elements of both tholos and rectangular tomb architecture.
The necropolis has yielded a wealth of grave goods, including pottery, stone vases, metal objects, jewelry, and figurines, providing insights into the social structures and religious beliefs of the Minoans. The variety of tomb types and grave goods reflects the prosperity and social complexity of the Archanes valley. The architectural features and artistic motifs found at Phourni resonate with those found at Knossos, indicating cultural homogeneity and interaction between these two important centers. The religious beliefs of the Minoans are also reflected in the finds at Phourni, with religious symbols and ritual objects suggesting a belief in an afterlife and elaborate burial rituals.
The Phourni necropolis is the richest burial site in Crete and provides a unique glimpse into the burial practices, social structures, and religious beliefs of the Minoan civilization.
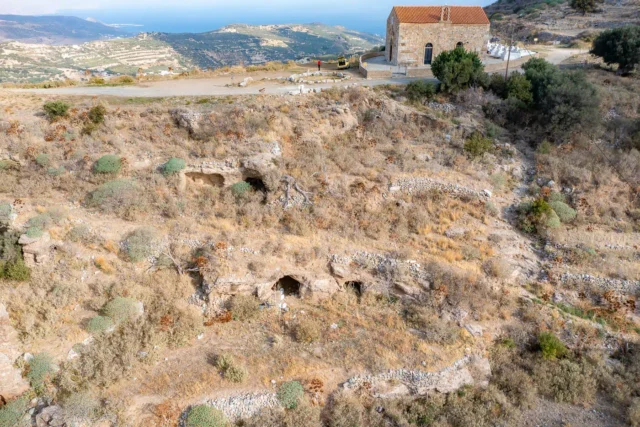
The Archaeological Site of Onithe
Onithe, an archaeological site near Goulediana in Rethymno, Crete, offers a glimpse into the island's history from the Neolithic period to the Venetian and Ottoman eras. Its strategic location on a plateau provided control over key passages and natural defenses. The site features ruins like the Acropolis with its pseudo-isodomic walls and tower, House A with its abundance of pottery and pithoi, an ancient spring and possible sanctuary, and a Paleochristian Basilica with well-preserved mosaics.
The ancient name of the city remains uncertain, with scholarly attempts to identify it as Osmida or Phalanna remaining inconclusive. It may have been an early settlement center for ancient Rhithymna. The site has yielded artifacts like pottery shards, a bronze zodiac, exquisite metalwork, and sculptures, providing evidence of its prosperity and cultural vibrancy throughout the Minoan, Archaic, Classical, Hellenistic, Roman, and Byzantine periods.
Olous
Olous, an ancient Cretan harbor city, now largely submerged off the coast of Elounda, was inhabited from the Early Minoan period through the Hellenistic period. Its strategic location in the Mirabello Gulf made it a significant maritime hub, connecting the Eastern and Western Mediterranean. Archaeological investigations, including underwater surveys, have revealed remnants of Minoan cemeteries, fortifications, and possible public buildings. The city's history is intertwined with that of other Cretan powers like Knossos and Lato. Olous was known for its temple to Britomartis and its connections with Ptolemaic Egypt. Today, the site offers a glimpse into Crete's rich maritime past.
Hierapytna
Hierapytna, located on the southern coast of Crete, was founded in the Geometric period (c. 9th century BC). The city was a major hub for trade and commerce in ancient times and played a significant role in the island's political and military affairs. Hierapytna flourished during the Hellenistic and Roman periods. It became part of the Byzantine Empire after the division of the Roman Empire. Following the Arab conquest of Crete in the 9th century, Hierapytna was abandoned. Modern archaeological investigations have revealed a wealth of information about the city, including its city walls, agora, temple, theater, and private houses.
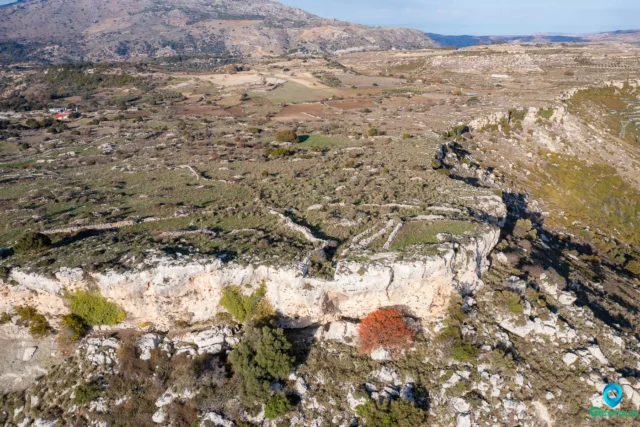
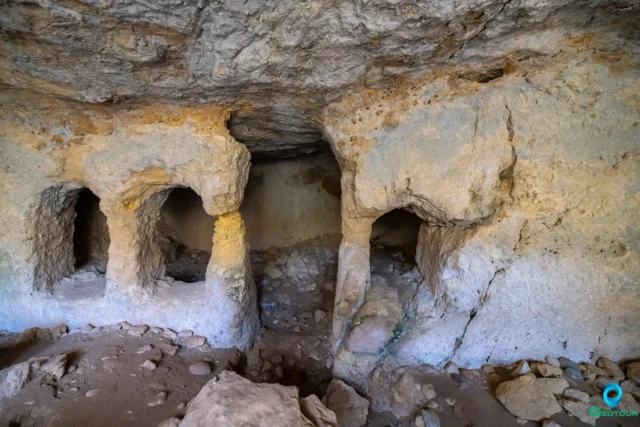
Siderospilia near Roufas
Siderospilia, meaning "Iron Caves," is a complex of three interconnected chambers carved into limestone bedrock near Roufas, Crete. Its purpose is debated, with theories ranging from blacksmith workshop to Roman-era burial site. Chamber 1 features a broken supporting column, roof opening, and stone bench. Chamber 2 is larger, with niches for burials. Chamber 3 resembles an early Christian church, with a dividing wall and door. Local legends link the cave to blacksmiths, ghosts, and eerie sounds. Some believe it was a dwelling before becoming a necropolis. The cave's location near a stream and possible ancient structures adds to its significance. Siderospilia is accessible but lacks official signage.
Dreros, ancient city
Dreros, also known as Driros, is an archaeological site near Neapoli in Crete, significant for its post-Minoan remains from the early Archaic Period. Flourishing from the 8th to 6th centuries BC, Dreros was an important center of trade and culture, known for its harbor, temples, bronze working, and pottery. The city, built on two hills, features a sanctuary dedicated to Apollo Delphinios, where 8th century BC bronze statuettes of Apollo, Artemis, and Leto were discovered. A large, open cistern, possibly used for ritual purposes, was found in the agora, the city's public gathering space. Inscriptions reveal a board of officials called the 'Twenty of the Polis' and the division of the people into 'phylai' or tribes. The site includes one of the earliest known examples of a Greek temple, dedicated to Apollo Delphinios. Dreros declined in importance after the 6th century BC and was eventually abandoned.
Ancient Elyros
Ancient Elyros, situated on Crete's 'Kefala' hill near Rodovani, originated in the Early Iron Age and thrived until Late Antiquity. Named after the mythical son of Apollo, it became a major urban center in southwestern Crete during the Classical period, known for trade and weapon manufacturing. As a leading city in the Oreioi League (formed in the 3rd century BC for security and economic reasons, including Hyrtakina, Lissos, Poikilasio, Syia, and Tarra), Elyros maintained external connections before the league's likely dissolution before 183 BC, a period when it was at war with Kydonia. The Roman era marked a time of flourishing for Elyros, evidenced by the "Philosopher of Elyros" statue. The city featured fortification walls, an aqueduct, cisterns, and a theater. Elyros minted its own coins, indicating autonomy, with emblems similar to Hyrtakina's. Its territory included the port of Lissos, a key economic contributor and religious center with an Asklepieion, as well as the coastal cities of Syia and Poikilasio. Archaeological findings suggest communication with mainland Greece, North Africa, and Southern Italy. Notably, Elyros had a local workshop producing unique glass pyxides. A rural sanctuary dedicated to Poseidon was also found in the 'Tsiskiana' area, likely under Elyros's jurisdiction.
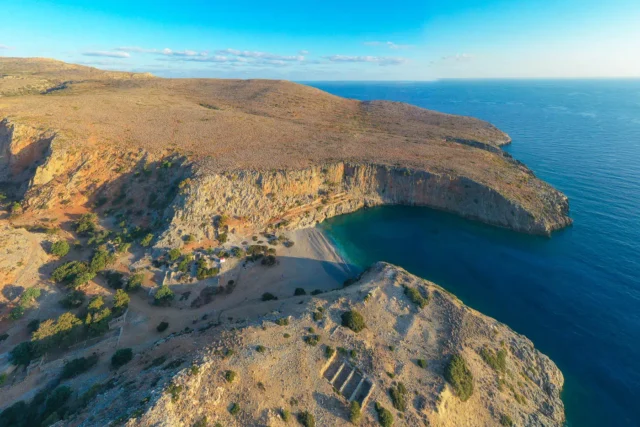
The Ancient Port of Lissos
Lissos, an ancient Cretan port city, was a vital healing center and trade hub. It served the inland cities of Elyros, Hyrtakina, and Tarra. The sanctuary of Asklepios attracted pilgrims seeking cures.
Hyrtakina
Hyrtakina, an ancient Cretan city, thrived in the Oreia region near the White Mountains. As a member of the League of the Oreioi, it played a role in regional security and economic development. The city's strategic location on 'Kastri' hill was fortified by double walls. Hyrtakina's autonomy is evident from its unique coinage, featuring a wild goat and a bee. Trade connections extended to mainland Greece, North Africa, and Southern Italy, as shown by archaeological finds. The city's peak was in the 4th century BC, coinciding with its coin minting. Hyrtakina's agreement with Cyrene for grain supply highlights its interaction with other Mediterranean cities. The city was abandoned in Roman times.
Polyrrhenia
An Ancient City of Western Crete Polyrrhenia, also known as Polyrrenion, was a city in ancient Crete, located on the northern coast of the western part of the island . […]
The Ancient City of Falasarna
An ancient city on western Crete, with history from the Neolithic (c. 3500 BCE) to its Roman conquest in 67 BCE. A fortified Hellenistic maritime power involved in trade and piracy, it rivaled Polyrrhenia. Excavations have uncovered a Temple of Demeter with Archaic Daedalic offerings and a 4th-century BCE fortified harbor. The harbor's towers were destroyed by the 365 CE earthquake. Today, the site is a protected archaeological park with ongoing research.
Minoan tholos tomb at Maleme
The Minoan tholos tomb at Maleme, Crete, is a remarkable example of Bronze Age funerary architecture. Located near the village of Maleme in western Crete, the tomb is known for […]
Rokka archaeological site
Located inland in Kissamos, western Crete, on the slopes of Troulli hill. This protected archaeological site dates to the Hellenistic period (4th-2nd century BC). Its identity is debated, possibly being the ancient city of Keraia or linked to the "Koinon ton Modaion." The settlement features unique architecture with houses, cisterns, and stairways carved into the limestone. A necropolis with rock-cut tombs has yielded artifacts. The modern village hosts the annual Giortes Rokkas festival to promote cultural heritage and repopulation.
Pergamos Ancient City
Pergamos (Πέργαμος) was a city of ancient Crete, founded in the 8th century BC. It was one of the hundred cities of Crete mentioned by Homer in his works. It […]
Katre, an Ancient City of Crete
Katre, an ancient city of Crete, is shrouded in mystery and intrigue. While historical and archaeological evidence about Katre is limited, its strategic location and mythological connections suggest a place […]